Financial Institutions and Their Role in India
Financial institutions play a critical role in an economy by managing money, providing loans, ensuring financial stability, and regulating markets. In India, there are various financial institutions, and they are responsible for different aspects of the economy, such as regulating monetary policy, overseeing financial markets, and supporting economic growth. Let’s break down the roles of the major financial institutions in India, like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and others.

1. Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
What is the RBI?
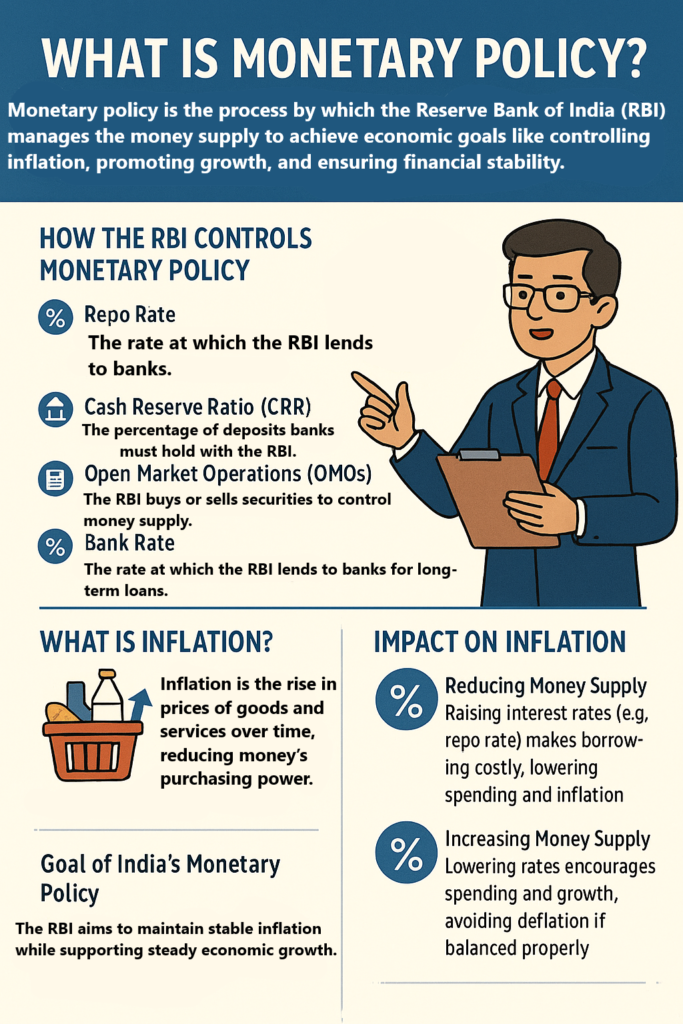
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India’s central bank, responsible for regulating the country’s monetary policy and ensuring the stability of the financial system.
Role of the RBI:
- Monetary Policy Control: The RBI controls the supply of money in the economy. It does this by adjusting interest rates (such as the repo rate) to control inflation, ensure economic growth, and stabilize the currency.
- Regulating Banks: The RBI supervises and regulates commercial banks and other financial institutions to ensure they follow the rules and maintain financial stability. It also manages the banking system.
- Currency Issuance: The RBI is the sole authority for issuing currency notes (except for one-rupee coins and notes, which are issued by the Ministry of Finance). It ensures the supply of currency meets the demand of the economy.
- Foreign Exchange Management: The RBI manages the foreign exchange reserves and facilitates international trade by regulating the value of the Indian Rupee against other currencies.
- Government’s Banker: The RBI works as the government’s banker, managing its accounts and executing government transactions.
2. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
What is SEBI?
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory authority that oversees the stock markets and ensures that securities markets operate fairly and transparently.
Role of SEBI:
- Regulating Stock Exchanges: SEBI regulates the stock exchanges (like the Bombay Stock Exchange and the National Stock Exchange) to make sure that trading is fair and transparent. It ensures that investors’ interests are protected.
- Protecting Investors: SEBI creates and enforces rules to protect investors from fraudulent activities, such as insider trading (when people use confidential information to make unfair profits in the stock market).
- Promoting Market Efficiency: SEBI aims to make the financial markets more efficient by improving transparency, reducing fraud, and ensuring that companies provide accurate financial information to investors.
- Regulating Mutual Funds: SEBI also regulates mutual funds (investment funds) and ensures that they follow strict rules to protect investors’ money.
3. Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC)
What is LIC?
- The Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) is the largest life insurance company in India, which provides various life insurance policies to individuals and businesses.
Role of LIC:
- Providing Life Insurance: LIC offers policies that provide financial protection to families in case of the death of the breadwinner. It also offers policies to provide income after retirement or savings options for the future.
- Investment: LIC invests the collected premiums into various financial assets like stocks, bonds, and government securities, contributing to the development of the economy.
- Promoting Savings and Investments: Through its various life insurance products, LIC encourages individuals to save and invest in long-term financial products for their future needs.
4. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
What is NABARD?
- NABARD is a government-owned bank that focuses on the development of the agriculture and rural sectors in India.
Role of NABARD:
- Providing Credit to Farmers: NABARD provides financial support to farmers and rural entrepreneurs to help them develop their farms, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Rural Development: NABARD works on improving rural infrastructure, such as irrigation systems, roads, and electricity, to support overall development in rural areas.
- Promoting Rural Innovation: NABARD encourages new technologies and innovations in agriculture and rural industries to improve productivity and livelihoods.
5. Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI)
What is IRDAI?
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) is the authority that regulates and oversees the insurance industry in India.
Role of IRDAI:
- Regulating Insurance Companies: IRDAI ensures that insurance companies operate fairly and meet legal requirements to protect the interests of policyholders.
- Promoting Insurance Sector Growth: The authority promotes the growth of the insurance sector by introducing new policies and regulations that encourage people to buy insurance and companies to innovate.
- Ensuring Fair Practices: It ensures that insurance providers are not engaging in unfair practices, such as exploiting customers or providing false information.
6. Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC)
What is FSDC?
- The FSDC is a body formed by the Indian government to monitor and promote the financial stability of the country.
Role of FSDC:
- Coordinating Regulatory Bodies: The FSDC coordinates between various financial regulators like the RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and others to ensure smooth functioning of the financial system.
- Financial System Stability: It helps in identifying risks and taking corrective actions to ensure that the financial system remains stable, especially during times of financial stress.
- Macro-Prudential Regulation: FSDC works on managing risks that affect the overall financial system, such as market crashes or banking crises.
7. Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
What is SIDBI?
- SIDBI is a financial institution that focuses on the growth and development of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in India.
Role of SIDBI:
- Providing Financial Support: SIDBI offers loans, financial products, and services specifically designed for small and medium businesses. It helps them grow and expand their operations.
- Promoting Entrepreneurship: SIDBI supports new entrepreneurs by offering credit facilities and guidance for setting up small businesses.
- Assisting with Technical Support: SIDBI provides training and technical support to SMEs to improve their productivity and efficiency.
Conclusion
In summary, financial institutions are crucial to the functioning of the economy. They help manage money, regulate financial markets, and ensure economic stability. Here are the main roles of the key financial institutions in India:
- RBI: Controls monetary policy, manages currency, and supervises banks.
- SEBI: Regulates stock markets and protects investors.
- LIC: Provides life insurance and promotes savings.
- NABARD: Focuses on rural development and agricultural financing.
- IRDAI: Regulates the insurance sector.
- FSDC: Ensures the stability of the financial system.
- SIDBI: Supports the growth of small and medium businesses.
Each of these institutions plays a unique role in helping the economy grow while keeping financial systems safe and stable for everyone.