What is Healthcare Technology?
Healthcare technology refers to the use of tools, devices, and systems that improve the quality, efficiency, and delivery of healthcare services. This includes everything from the machines used in hospitals to the software programs that help doctors keep track of patient records.
In simple terms, it’s all the tech innovations that help doctors, nurses, and healthcare professionals do their jobs better and help patients get better care.
Why is Technology Important in Modern Healthcare?
- Improving Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Technology helps doctors diagnose diseases more accurately and quickly. For example, X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans use advanced machines to create images of the inside of the body. This helps doctors see problems like broken bones, tumors, or other health issues.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also helping doctors by analyzing medical data and suggesting possible diagnoses. AI can even help doctors find patterns in diseases that might be hard to spot without technology.
- Better Access to Health Information:
- Thanks to electronic health records (EHR), all of a patient’s medical history is stored digitally. Doctors and healthcare workers can access this information instantly, even if a patient visits a different hospital or clinic. This makes it easier for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about a patient’s treatment.
- Patients can also access their own health records online, making it easier to track their health progress and communicate with their doctors.
- Telemedicine: Healthcare from a Distance:
- Telemedicine allows patients to consult with doctors over the phone or through video calls, which is super helpful for those who live in rural or remote areas where it’s hard to access healthcare services. Patients no longer need to travel long distances for a simple consultation.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth became extremely popular as people could get medical advice from the safety of their homes.
- Robotic Surgery:
- Robotic surgery uses robots to help doctors perform surgeries with more precision. Robots can perform minimally invasive procedures, meaning doctors can make smaller cuts. This leads to faster recovery, less pain, and fewer complications for patients.
- For example, the da Vinci Surgical System allows surgeons to perform surgeries remotely with the help of robotic arms that are controlled by a computer.
- Wearable Health Devices:
- Wearable technology, like smartwatches or fitness trackers (e.g., Fitbit or Apple Watch), helps people keep track of their health in real time. These devices can measure things like your heart rate, blood pressure, sleep patterns, and even detect irregularities that might signal health problems.
- Some devices can even alert doctors or healthcare providers if something goes wrong, helping prevent serious health issues before they become emergencies.
- Personalized Medicine:
- Thanks to technology, doctors can now offer personalized treatment based on a person’s genetics, lifestyle, and health history. This is called precision medicine.
- For example, if a patient has a certain type of cancer, doctors can use genetic testing to figure out the best medicine or treatment plan specifically for that person, rather than using the same treatment for everyone.
- Data Collection and Analytics:
- Healthcare systems now use big data to analyze patient information, trends, and outcomes. This data helps healthcare providers understand diseases better, predict outbreaks, and improve treatment methods. For example, data can help predict flu outbreaks, allowing hospitals to prepare in advance.
- Analyzing data from millions of patients can also help improve public health policies and prevent diseases.
- Drug Development and Research:
- Technology plays a huge role in the research and development of new medicines and treatments. With advanced computers, 3D printing, and AI, researchers can create new drugs faster and more efficiently than ever before.
- For instance, the rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines was made possible by new technologies that allowed researchers to test and develop vaccines much faster than traditional methods.
- AI and Machine Learning:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (a type of AI that learns from data) are helping in the healthcare sector by analyzing huge amounts of medical data to identify patterns that human doctors might miss. For example, AI can be used to analyze medical images (like X-rays or MRIs) and detect diseases like cancer or heart conditions early.
- AI can also help doctors predict how a patient will respond to certain treatments, improving the chances of recovery.
- Improving Efficiency and Reducing Costs:
- Technology helps healthcare systems run more efficiently by automating administrative tasks like scheduling appointments, billing, and managing patient records. This frees up healthcare workers to focus more on patient care.
- By reducing errors and improving patient outcomes, technology also helps reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
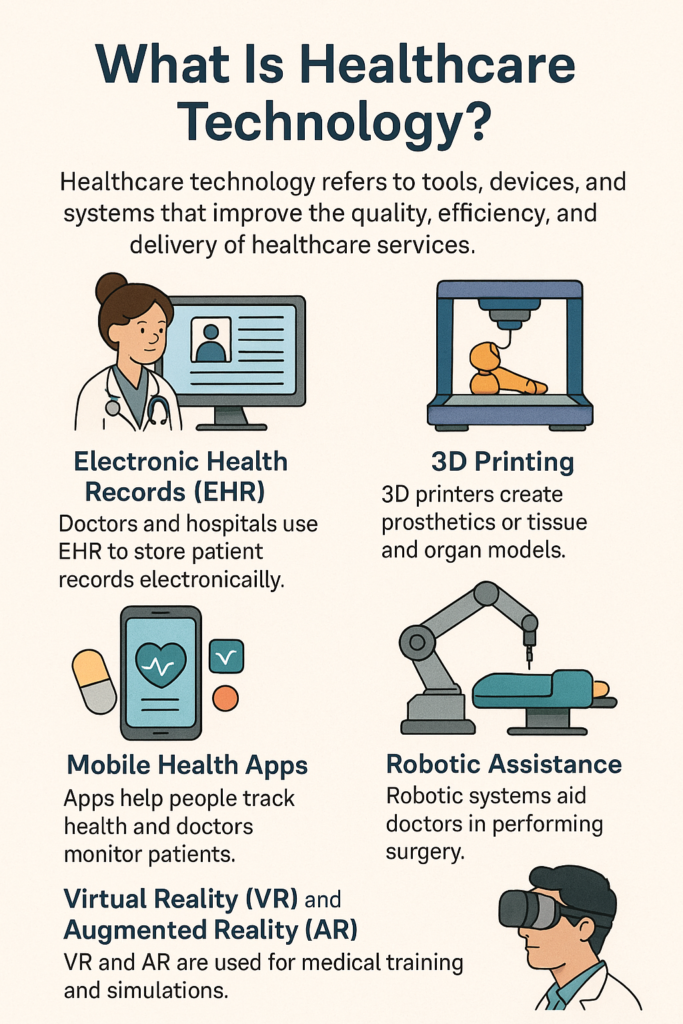
Examples of Technology in Healthcare
- Electronic Health Records (EHR):
- Doctors and hospitals use EHR to store patient records electronically. Instead of using paper files, which can be lost or hard to read, everything is stored digitally, making it easy for doctors to access important information quickly.
- 3D Printing:
- 3D printers are being used to create prosthetics (artificial limbs) or even tissue and organ models for surgeons to practice on before performing real surgeries. This technology helps improve the accuracy of surgeries and reduces the risk of complications.
- Mobile Health Apps:
- There are many mobile apps that help people track their health and wellness. For example, apps can track your diet, exercise, sleep patterns, and remind you to take your medication.
- Some apps even allow doctors to remotely monitor patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease, making it easier to manage these conditions.
- Robotic Assistance:
- Robotic systems like the da Vinci Surgical System or robot-assisted rehabilitation devices help doctors perform surgeries with more precision, and help patients with rehabilitation by assisting with physical therapy exercises.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):
- VR and AR technologies are being used to help with medical training and surgery simulations. Medical students can practice complex surgeries in a virtual environment before doing them in real life.
- Surgeons also use AR during surgery to get real-time information or 3D images of the patient’s body, helping them make better decisions.
Challenges of Technology in Healthcare
While technology in healthcare is incredibly useful, there are a few challenges that come with it:
- Cost: Implementing new technology can be expensive. Not all hospitals, especially in low-income areas, can afford the latest tech.
- Privacy and Security: Storing patient data electronically raises concerns about privacy. There is always the risk that hackers could steal sensitive patient information. This is why it’s important to have strong data protection systems in place.
- Training: Healthcare professionals need to be properly trained to use new technology. Sometimes, they may face difficulty adapting to advanced systems or machines, especially in rural or underdeveloped areas.
- Dependence on Technology: Over-reliance on technology might lead to doctors and healthcare providers depending too much on machines and algorithms instead of their own judgment and experience.
Conclusion
Technology is revolutionizing healthcare by making it more efficient, accessible, and personalized. From helping doctors diagnose diseases more accurately to enabling remote consultations through telemedicine, technology is transforming the way we receive medical care.
While there are challenges like cost and privacy concerns, the overall impact of technology in healthcare is overwhelmingly positive, making it one of the most exciting fields to watch as it continues to evolve. As technology advances, we can expect even more breakthroughs that will improve health outcomes and make healthcare services available to more people, especially in underserved areas.











