The Evolution of Computers: From Mainframes to Personal Devices
Computers have come a long way since their invention. They’ve evolved from large machines that only big companies or governments could use, to personal devices that we carry in our pockets today. Let’s look at how computers developed, step by step.
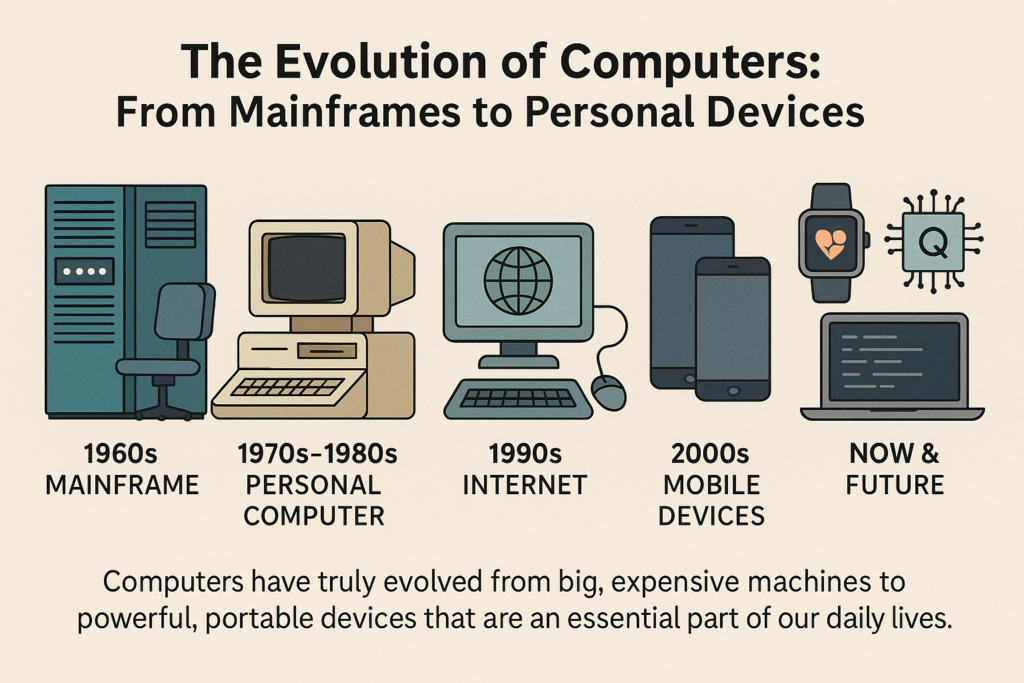
1. The Early Beginnings (Before Modern Computers)
Before computers as we know them existed, humans used simple tools like the abacus for calculations. The first true mechanical calculating machine was invented by Charles Babbage in the 1830s, known as the Analytical Engine. While this machine wasn’t fully built, it laid the groundwork for modern computing ideas.
2. The First Computers (1940s – 1950s)
In the 1940s, the first electronic computers were developed. These were huge, complicated machines used for tasks like calculations, and they filled entire rooms.
- ENIAC (1945): One of the earliest computers, ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), was used by the U.S. military for calculations during World War II.
- Mainframes: These early computers were known as mainframes. They were massive, expensive, and could only be used by large organizations like governments or universities. They took up entire rooms and required special, trained operators to use.
3. The Rise of Transistors and Miniaturization (1950s – 1960s)
In the 1950s and 1960s, computers began to get smaller and more powerful, thanks to a major invention: the transistor.
- Transistors: Before transistors, computers used vacuum tubes, which were bulky and often broke. Transistors were smaller, more reliable, and used less power. This allowed computers to become more efficient and less expensive.
- Mainframes Shrink: With the invention of transistors, the size of computers started to shrink. Companies began making minicomputers—still large, but smaller than the older mainframes. These were used by smaller businesses, not just large corporations or governments.
4. The Birth of Personal Computers (1970s – 1980s)
In the 1970s, technology took another huge leap: personal computers were invented. These were computers small enough for individuals or small businesses to afford and use.
- 1970s – The First Personal Computers: Companies like Apple, IBM, and Microsoft started creating personal computers. The Apple I and Apple II, made by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, were among the first successful personal computers. They were still expensive, but they were now within reach of everyday people.
- 1980s – IBM and Microsoft: IBM introduced the IBM PC in 1981, which became very popular. The Windows operating system by Microsoft, released in 1985, made personal computers much easier to use with a graphical interface (the screen with pictures and icons we use today).
- Laptops: In the 1980s, the first laptops were also introduced, making computers even more portable. They were still quite large, but they were the beginning of the mobile computing we rely on today.
5. The Internet and the Digital Revolution (1990s – Early 2000s)
By the 1990s, computers were becoming much faster and more common in homes and businesses, and the internet started to take off. This changed everything.
- The Internet Boom: The internet allowed computers to connect with each other globally. People could now browse websites, send emails, and shop online. This created a whole new world of possibilities.
- Better Performance: Personal computers got much more powerful, with faster processors, larger memory, and better graphics. The Windows 95 operating system was introduced, which made using computers even easier for everyone.
- Affordable PCs: Computers became more affordable for the average person, and people began having them in their homes, schools, and offices.
6. The Rise of Mobile Devices (2000s – Present)
In the 2000s, a new kind of computer appeared: smartphones and tablets. These devices were even smaller and more portable than laptops, and they offered a lot of the same functions.
- Smartphones: The iPhone, released in 2007, revolutionized the world by combining a phone, computer, camera, and music player into one device. Other companies like Samsung followed suit with their own smartphones. These devices are now used for almost everything: browsing the internet, social media, gaming, shopping, and more.
- Tablets: Devices like the iPad (released in 2010) introduced a new way to use computers. Tablets are like smaller laptops, but they don’t have a keyboard and rely on touch screens.
- Cloud Computing: With the rise of cloud technology, people can now store and access data and software on the internet, rather than just on their computers. This has made computers even more flexible and powerful.
7. Modern Computers: Small, Powerful, and Everywhere (2010s – Present)
Today, computers are not just in our homes and offices—they are everywhere.
- Wearables: We now have smartwatches and fitness trackers that connect to our phones, providing us with health data and notifications.
- Supercomputers: For complex tasks like scientific research, weather forecasting, or simulations, supercomputers have become even more powerful. These are used by governments, research institutions, and big companies to solve problems that require immense computing power.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Computers are now getting smarter. AI and machine learning allow machines to learn from data and make decisions. This has led to developments in things like self-driving cars, personal assistants (like Siri or Alexa), and advanced robotics.
8. The Future of Computers
The future of computers is exciting, with ongoing advancements in technology:
- Quantum Computers: These are still in the early stages, but they promise to be exponentially faster than today’s computers. They could solve problems that are impossible for current computers.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: As computers get more advanced, we might use virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) to interact with the digital world in new, immersive ways.
- Smarter Devices: We’re likely to see more devices that think and act like humans, with artificial intelligence helping us in everything from healthcare to entertainment.
In Summary:
Computers started out as huge machines used only by governments and large businesses, but over time they got smaller, faster, and cheaper. In the 1970s and 1980s, personal computers became available for individuals and small businesses. In the 1990s, the internet transformed the way we use computers. By the 2000s, mobile devices like smartphones and tablets became the new norm. Today, computers are everywhere, from wearables to supercomputers, and the future promises even more exciting innovations with AI, quantum computing, and virtual reality.
Computers have truly evolved from big, expensive machines to powerful, portable devices that are an essential part of our daily lives.











