1. Liberalism
What is Liberalism?
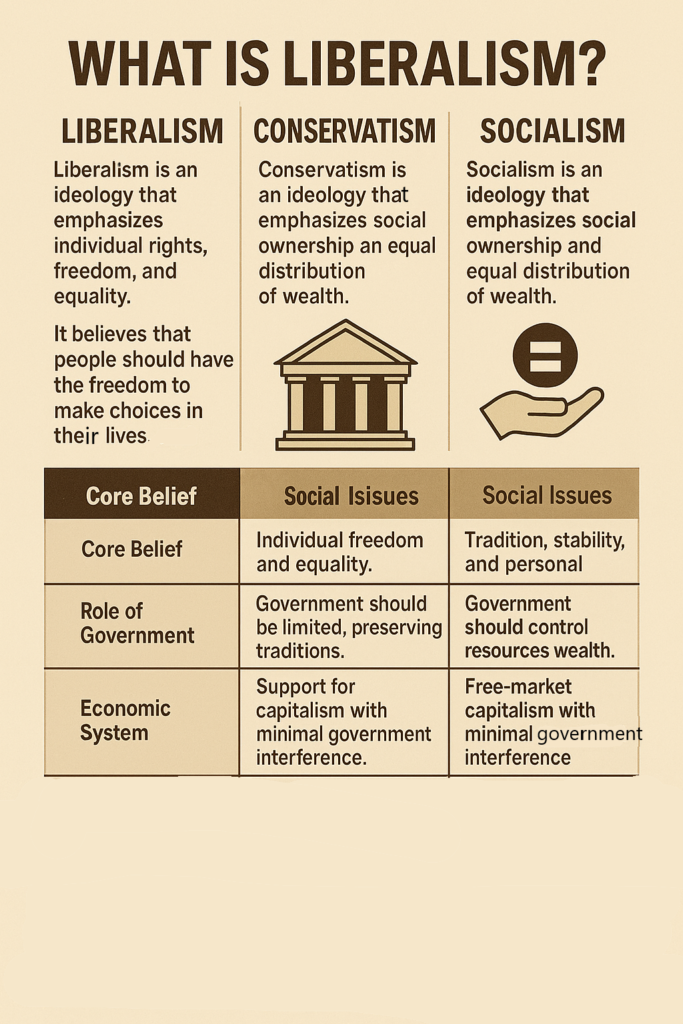
- Liberalism is an ideology that emphasizes individual rights, freedom, and equality. It believes that people should have the freedom to make choices in their lives, and the government should protect those freedoms.
Key Beliefs of Liberalism:
- Individual Rights: Liberals believe that every person has the right to freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and the right to participate in society without fear of discrimination.
- Equality: Liberals want a society where people are treated equally, regardless of their background, race, or gender.
- Social Progress: Liberals tend to support change and progress in society, whether that’s through education, technology, or social reforms.
- Government’s Role: The government should play an active role in ensuring fairness and helping those in need, but it should not control every part of life.
Examples of Liberalism:
- In practice, liberalism is often seen in countries that support democratic values, social welfare programs, and a free market economy with some regulation. Countries like the United States, Canada, and many European countries have liberal elements in their politics.
2. Conservatism
What is Conservatism?
- Conservatism is an ideology that emphasizes tradition, stability, and limited government. Conservatives believe that society should change slowly and that traditional values are important for maintaining a strong community.
Key Beliefs of Conservatism:
- Tradition and Stability: Conservatives value traditional customs and beliefs that have been passed down through generations, such as respect for family, religion, and national heritage.
- Limited Government: Conservatives believe that the government should not interfere too much in people’s lives or businesses. They support free-market economies where businesses and individuals make decisions without heavy government regulation.
- Personal Responsibility: Conservatives emphasize the importance of personal responsibility, meaning individuals should work hard and take care of themselves without relying too much on government assistance.
- Respect for Authority: Conservatives often believe in the importance of law and order, and that society works best when people respect rules, institutions, and leaders.
Examples of Conservatism:
- Conservative policies are often seen in countries with a focus on national security, traditional values, and minimal government intervention. For example, the United States (especially the Republican Party) and the United Kingdom have conservative elements.
3. Socialism
What is Socialism?
- Socialism is an ideology that emphasizes social ownership and equal distribution of wealth. Socialists believe that wealth and resources should be shared more equally among all people, and that everyone should have access to basic needs like education, healthcare, and housing.
Key Beliefs of Socialism:
- Equality and Fairness: Socialists believe that everyone should have the same opportunities and access to resources, regardless of their wealth or background.
- Collective Ownership: Socialists support collective or government control over industries and resources, so that profits and benefits are shared fairly, instead of a few people or corporations controlling everything.
- Social Welfare: Socialism promotes public services (like healthcare, education, and social security) to ensure everyone’s needs are met. This includes taxes that help fund social programs.
- Cooperation Over Competition: Socialists believe in working together to create a better society, rather than focusing on competition between individuals or businesses.
Examples of Socialism:
- Socialism is often seen in countries like Cuba, Venezuela, and North Korea, where the government controls key industries. In other countries, socialist policies are mixed with capitalism, such as in Sweden and Norway, where free market economies exist alongside generous social safety nets.
Comparison of the Three Ideologies
| Feature | Liberalism | Conservatism | Socialism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Individual freedom and equality. | Tradition, stability, and personal responsibility. | Equality and social ownership. |
| Role of Government | The government should protect freedoms, but allow individual choice. | Government should be limited, preserving traditions. | Government should control resources and distribute wealth equally. |
| Economic System | Support for capitalism with some regulation. | Free-market capitalism with minimal government interference. | Government controls or regulates key industries, with public ownership. |
| Social Issues | Supports social reforms and progress. | Values traditional family values and social norms. | Focuses on redistribution of wealth and social equality. |
Summary:
- Liberalism: Believes in individual freedom, equality, and progressive change. The government should protect rights and provide some support to people, but should not control everything.
- Conservatism: Emphasizes tradition, stability, and personal responsibility. Conservatives prefer a limited government that does not interfere much in personal life and the economy.
- Socialism: Focuses on equality and social ownership. Socialists believe that resources should be shared equally among everyone and that the government should help meet the basic needs of all citizens.
Each ideology reflects different beliefs about how society should work and how resources should be distributed, and they all shape political systems around the world.











