1. Atomic Structure
The atomic structure is like the blueprint of an atom, which is the smallest unit of matter that makes up everything around us.
- What is an Atom?
An atom is made up of three main particles:- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the nucleus (the center of the atom).
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also found in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
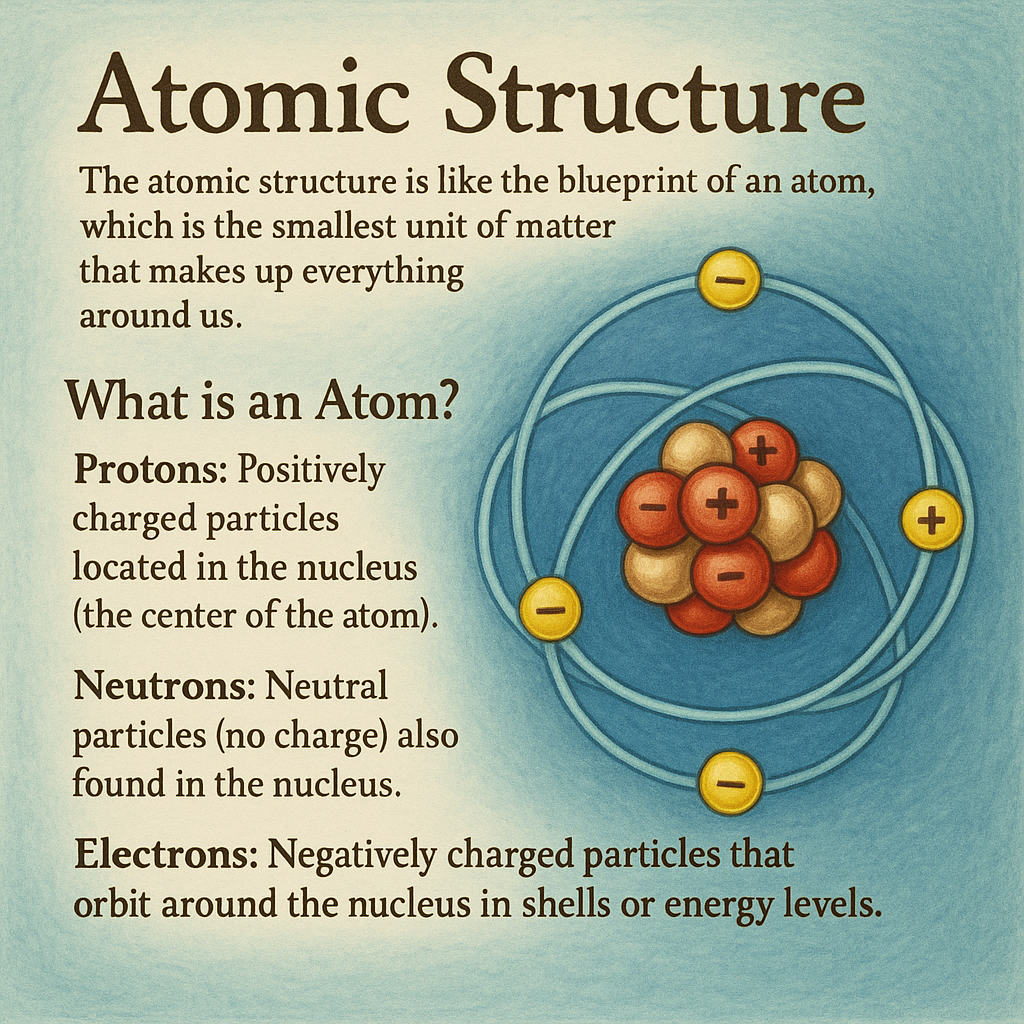
How is an Atom Structured?
- The nucleus (center of the atom) contains protons and neutrons.
- The electrons move around the nucleus in orbits (like planets orbiting the sun). These orbits are divided into energy levels (shells).
- The number of protons in the nucleus determines what element the atom is. For example:
- Hydrogen has 1 proton,
- Oxygen has 8 protons.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
- The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom, which also equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
- The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Example:
- In a Carbon (C) atom:
- Atomic number = 6 (because it has 6 protons)
- Mass number = 12 (because it has 6 protons and 6 neutrons)
2. Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies carbon-based compounds. Almost all living things are made up of organic compounds, so organic chemistry is very important for life.
- What Makes a Compound Organic?
A compound is organic if it contains carbon atoms. In organic compounds, carbon atoms bond with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.
Key Features of Organic Compounds:
- Carbon atoms can form strong bonds with other carbon atoms, which allows for the creation of large and complex molecules (like those in living organisms).
- Organic compounds can be simple (like methane – CH₄) or complex (like DNA – a huge molecule with carbon atoms).
Common Organic Compounds:
- Hydrocarbons: Compounds made only of carbon and hydrogen. They can be:
- Alkanes: Simple hydrocarbons with single bonds, e.g., methane (CH₄).
- Alkenes and Alkynes: Hydrocarbons with double or triple bonds, e.g., ethene (C₂H₄) or ethyne (C₂H₂).
- Functional Groups: These are specific groups of atoms that give compounds their chemical properties. For example:
- Alcohols (contains –OH group, like ethanol (C₂H₅OH)).
- Carboxylic Acids (contains –COOH group, like acetic acid (CH₃COOH)).
Why is Organic Chemistry Important?
- Life: All living organisms are made from organic compounds (like proteins, fats, and sugars).
- Everyday Products: Things like plastics, medicines, food, and fuels are made from organic chemistry.
3. Chemical Reactions
A chemical reaction happens when substances change into new substances. This happens because the atoms of the original substances rearrange to form new substances with different properties.
What Happens During a Chemical Reaction?
- Bonds Break: The bonds between atoms in the reactants (starting substances) are broken.
- New Bonds Form: New bonds are made between the atoms to create the products (new substances).
Basic Types of Chemical Reactions:
- Combination Reaction: Two or more substances combine to form one new substance.
- Example:
(Hydrogen + Oxygen = Water)
- Example:
- Decomposition Reaction: A single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
- Example:
(Hydrogen Peroxide breaks down into Water and Oxygen)
- Example:
- Displacement Reaction: One element displaces another in a compound.
- Example:
(Zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate)
- Example:
- Combustion Reaction: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
- Example:
(Methane + Oxygen = Carbon dioxide + Water + Heat)
- Example:
Balancing Chemical Equations:
In a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. This is called balancing the equation. For example:
- In the reaction
there are 4 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms on both sides, so it’s balanced.
Why are Chemical Reactions Important?
- Energy Production: Reactions like combustion (burning fuel) release energy that powers cars, factories, and homes.
- Life Processes: Many reactions happen inside our bodies (like digestion), helping us live and function.
- Everyday Products: Chemical reactions are used to make everything from soap to medicines to cleaning products.
Key Takeaways
- Atomic Structure:
- Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- The atomic number tells you how many protons are in an atom, which determines the element.
- Organic Chemistry:
- The study of carbon-based compounds.
- Organic compounds are the building blocks of life and many everyday products.
- Chemical Reactions:
- Chemical reactions change substances by rearranging atoms.
- There are different types of reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, and combustion.