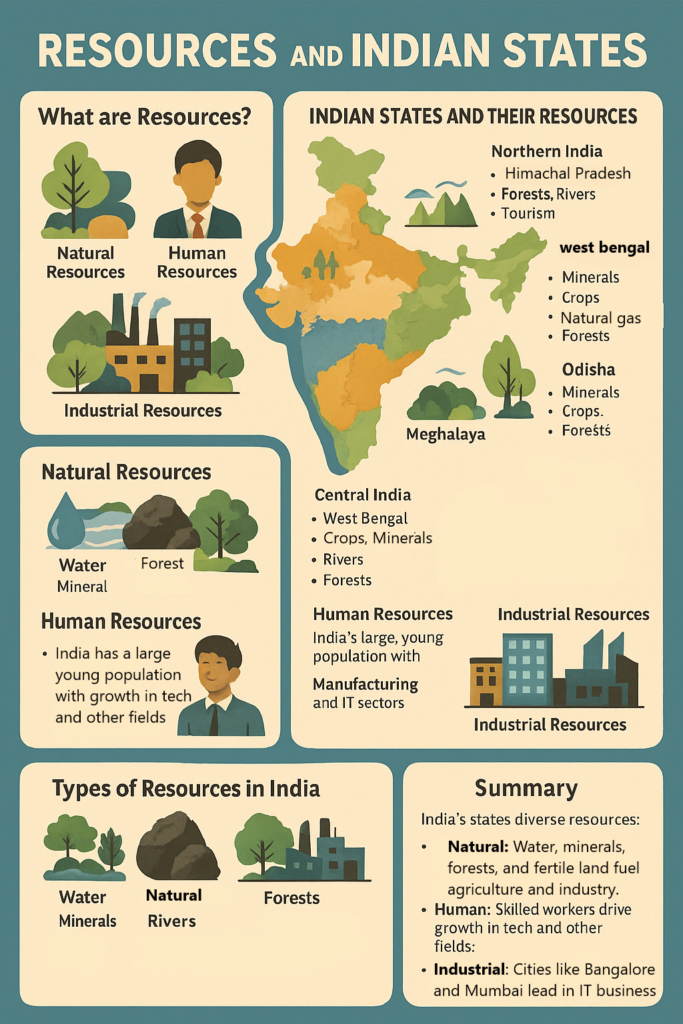
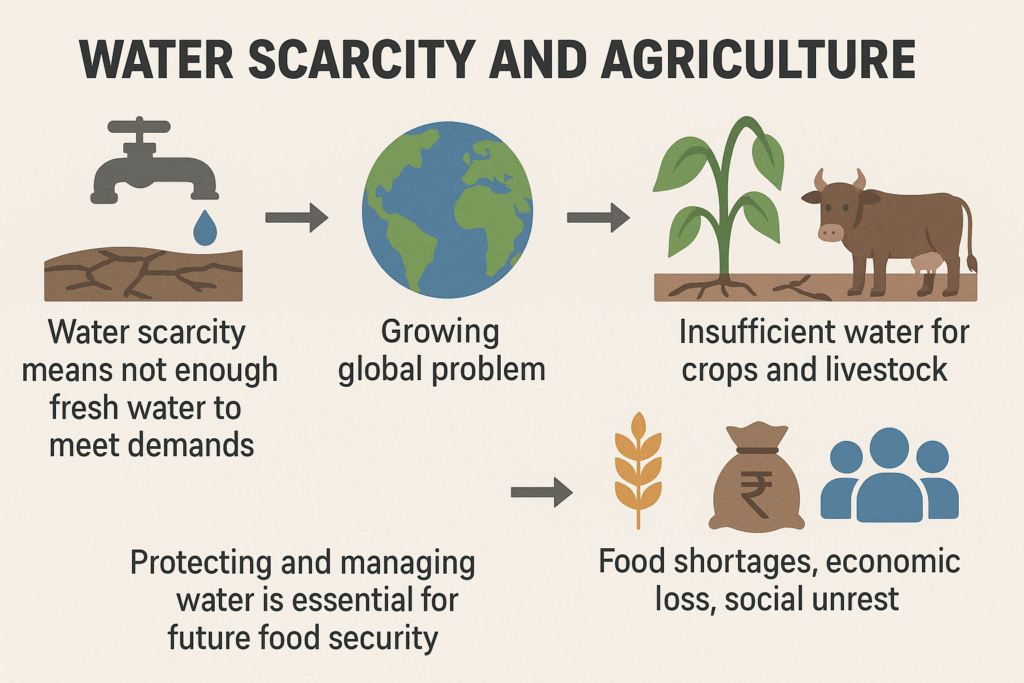
What is Sustainable Agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture is a way of farming that meets our current food needs without harming the environment or depleting resources for future generations. It focuses on using farming practices that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible. The goal is to grow food in a way that protects the planet while ensuring we can continue to produce enough food for everyone in the future.

Why is Sustainable Agriculture Important for Global Food Security?
Global food security means that everyone, everywhere, has enough food that is nutritious, safe, and accessible. But with the world’s population growing and climate change causing problems, it’s becoming harder to produce enough food for everyone. Sustainable agriculture is essential to solving this problem because it helps us:
- Produce food in a way that doesn’t damage the land.
- Preserve resources like water and soil for future farming.
- Protect the biodiversity (different plants and animals) that supports healthy ecosystems.
Key Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Here are some common sustainable agriculture practices that help ensure long-term food security:
1. Crop Rotation
- What it is: Crop rotation means changing the types of crops grown in a field each season instead of planting the same crop every year.
- Why it helps: Different crops take different nutrients from the soil. Rotating crops helps keep the soil healthy and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. It also helps control pests and diseases because they can’t easily build up when the crops are changed.
2. Agroforestry
- What it is: Agroforestry involves planting trees alongside crops or livestock. These trees can provide benefits like shade, wind protection, and extra income from fruit, timber, or other tree products.
- Why it helps: Trees help improve soil quality, reduce erosion, and provide a habitat for wildlife. They also store carbon, which helps fight climate change.
3. Conservation Tillage
- What it is: Conservation tillage is when farmers reduce how much they plow or disturb the soil. This can be done by leaving crop residues (like stalks or leaves) on the ground after harvest.
- Why it helps: It helps prevent soil erosion, improves water retention, and keeps the soil rich in nutrients. This method also reduces the amount of fuel and labor needed for plowing, making it more cost-effective.
4. Organic Farming
- What it is: Organic farming is a method of farming that avoids using synthetic chemicals like pesticides and fertilizers. Instead, it uses natural methods like compost, crop rotation, and natural pest control.
- Why it helps: Organic farming is better for the environment because it avoids chemicals that can pollute the water and soil. It also supports biodiversity and helps protect the health of farmers and consumers.
5. Water Conservation and Management
- What it is: Water conservation involves using water efficiently, reducing waste, and making sure crops get the water they need without overusing it.
- Why it helps: Water is a limited resource, especially in areas with droughts or water shortages. Techniques like drip irrigation (delivering water directly to plant roots) or rainwater harvesting (collecting and storing rainwater) can help farmers use water more wisely.
6. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- What it is: IPM is a way of controlling pests that uses a combination of methods, such as biological control (using natural predators), physical barriers, and crop rotation, instead of just spraying chemicals.
- Why it helps: It reduces the use of harmful pesticides, protects pollinators (like bees), and helps maintain a healthy ecosystem. It also reduces costs for farmers because they don’t have to buy expensive chemicals.
7. Permaculture
- What it is: Permaculture is a system of farming that mimics natural ecosystems. It involves creating self-sustaining, low-maintenance farming systems that work in harmony with nature.
- Why it helps: It focuses on building soil health, conserving water, and creating a diverse, resilient farming system that can withstand changing conditions.
8. Reducing Food Waste
- What it is: This practice focuses on reducing waste at all stages—during production, distribution, and consumption. This includes better storage, efficient harvesting, and using leftovers.
- Why it helps: Reducing food waste means less food is thrown away, and more people can be fed. It also helps reduce the environmental impact of food production, because growing food takes resources like water, land, and energy.
Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture for Food Security
- Improved Soil Health: Practices like crop rotation and organic farming help maintain healthy soil, which is essential for growing crops over the long term.
- Conserves Water: Efficient water use through practices like drip irrigation ensures that crops get enough water without wasting it. This is especially important in areas facing droughts.
- Increases Resilience to Climate Change: Sustainable farming practices help farmers adapt to changing weather patterns and extreme events like floods or droughts. For example, agroforestry and conservation tillage can protect soil and crops during heavy rainfall.
- Supports Biodiversity: By maintaining a variety of plants, animals, and ecosystems, sustainable agriculture helps protect biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem health and long-term food production.
- Reduces Dependence on Chemicals: Sustainable farming practices use fewer synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which reduces pollution and helps protect the health of farmers and consumers.
Examples of Sustainable Agriculture Around the World
- The System of Rice Intensification (SRI): This method is used in many countries to grow rice in a more sustainable way. It involves planting fewer seedlings and using less water, which improves yields and reduces environmental damage.
- Agroecology in Latin America: Farmers in countries like Brazil and Cuba are using agroecology, which focuses on farming practices that are both productive and environmentally friendly. This includes using organic inputs, preserving native plant species, and managing land sustainably.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) in India: ZBNF is a method of farming that reduces costs by using organic fertilizers, compost, and natural pest control. It has helped improve yields while reducing the use of expensive chemicals.
Challenges to Sustainable Agriculture
- Economic Barriers: Some farmers may not have the money to switch to sustainable practices or buy organic inputs, especially in poorer regions.
- Lack of Knowledge: Sustainable agriculture requires knowledge and training. Farmers need to learn new techniques and understand how to manage their land in an environmentally-friendly way.
- Climate Change: Extreme weather events like floods, droughts, and heatwaves can still threaten food production, even with sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Sustainable agriculture is crucial for ensuring global food security in the future. By using practices that protect the environment, conserve resources, and improve food production, we can ensure that there is enough food for everyone while also protecting the planet. While there are challenges, such as economic barriers and the impacts of climate change, sustainable farming offers a path toward a healthier, more resilient food system. It’s about farming in a way that works with nature, not against it.