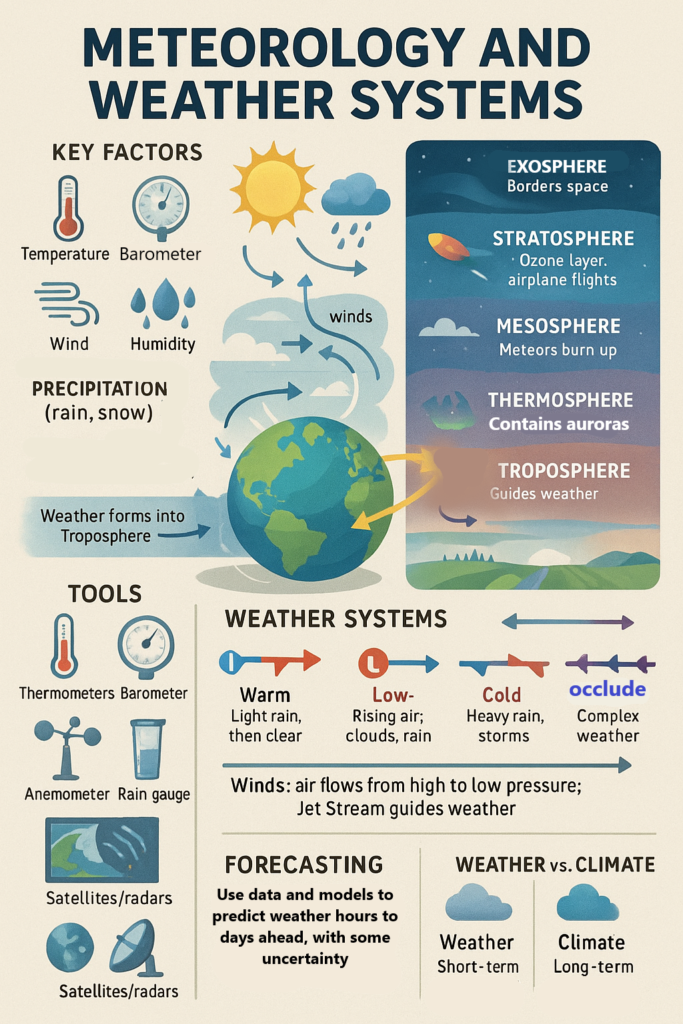
Ocean currents are like rivers of water that move across the ocean. These currents can flow horizontally (along the surface) or vertically (up and down). They are caused by a combination of wind, Earth’s rotation, and temperature differences in the water.
Imagine the ocean as a giant moving conveyor belt. Just like how a conveyor belt moves things from one place to another, ocean currents move warm and cold water across the globe. These currents affect many things on Earth, from weather patterns to marine life.
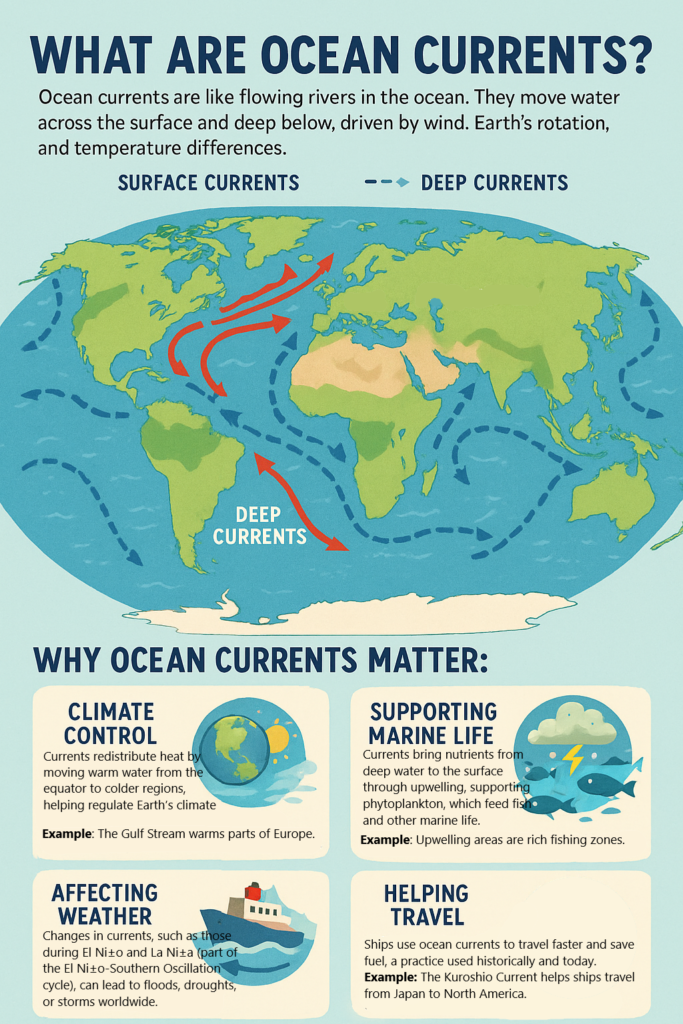
Types of Ocean Currents:
- Surface Currents: These are the currents that flow on the top layer of the ocean, driven mainly by wind. They can move warm water from the equator to colder regions and cold water from the poles to warmer areas.
- Deep (Thermohaline) Currents: These are slower currents that move deep under the ocean, driven by differences in water temperature and salinity (saltiness). These currents help mix the ocean’s water, distributing heat and nutrients.
How Do Ocean Currents Affect the World?
Ocean currents have a huge impact on weather, climate, and marine ecosystems. Let’s break it down:
1. Regulating Climate and Weather Patterns
- What it is: Ocean currents help control the temperature of the Earth by transferring heat from the equator (where it’s warm) to the poles (where it’s cold), and vice versa. This process helps balance global temperatures.
- Example: The Gulf Stream, a warm ocean current, flows from the Gulf of Mexico to Europe, making places like Northwestern Europe warmer than other regions at the same latitude.
2. Influencing Marine Life
- What it is: Ocean currents also carry nutrients from the deep ocean to the surface. These nutrients are essential for the growth of marine plants like plankton, which form the base of the ocean food chain.
- Example: Cold upwelling currents bring nutrient-rich water to the surface, which supports fish populations and larger marine life like whales, dolphins, and seals.
3. Affecting Weather Systems
- What it is: Ocean currents play a major role in the formation of weather patterns. For example, the El Niño and La Niña events are changes in ocean currents that affect weather all over the world.
- El Niño: When the Pacific Ocean current weakens, it can cause warmer-than-normal water, leading to droughts or floods in different parts of the world.
- La Niña: This happens when the waters of the Pacific Ocean are colder than usual, causing different weather effects like stronger storms.
4. Impacting Shipping and Travel
- What it is: Ocean currents are important for shipping routes and travel. Ships can use certain ocean currents to help them move faster across the oceans, saving time and fuel.
- Example: The Kuroshio Current helps ships travel from Japan toward North America more quickly.
5. Sea Level and Coastal Impact
- What it is: Changes in ocean currents can also impact the sea level and coastal areas. When warm water moves toward the poles, it can cause sea levels to rise, which can impact coastal communities.
- Example: The melting of polar ice can disrupt current patterns and raise sea levels, causing flooding in places near the ocean.
Summary:
Ocean currents are like massive rivers in the sea that move warm and cold water around the world. They help regulate climate, affect marine life, and influence weather patterns. Currents like the Gulf Stream make regions warmer, while changes in currents like El Niño can cause major weather shifts. They also play a role in shipping, sea levels, and coastal ecosystems. Understanding ocean currents is crucial because they connect many parts of the Earth’s systems and impact daily life.