In the world of power electronics, an inverter is a device that converts Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC). This conversion is crucial because while many sources like batteries and solar panels provide DC power, most household appliances and the electrical grid use AC power.
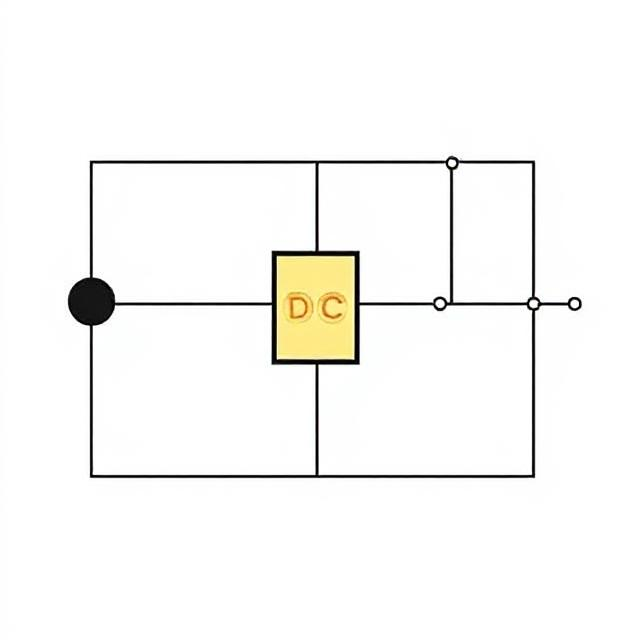
What is an Inverter?
An inverter takes a DC voltage as input and produces an AC voltage output. It “inverts” the power flow direction and waveform type — hence the name.The quality, shape, and frequency of the AC output depend on the inverter design and application requirements.
Why Are Inverters Important?
-
Renewable Energy: Solar panels generate DC power, but homes and grids use AC power.
-
Backup Power: Batteries store DC, which must be converted to AC during outages.
-
Electric Vehicles: Batteries provide DC, but electric motors run on AC.
-
Portable Devices: Some electronics need AC power from DC battery sources.
Types of Inverters
1. Square Wave Inverter
-
Output: Produces a simple square-shaped AC waveform.
-
Advantages: Very simple and inexpensive to build.
-
Disadvantages: Poor output quality, creates noise and harmonics, not suitable for sensitive equipment.
-
Applications: Simple tools, basic lighting, or devices tolerant of waveform distortion.
2. Modified Sine Wave Inverter
-
Output: Produces a stepped waveform that approximates a sine wave.
-
Advantages: Better than square wave, more efficient and compatible with many appliances.
-
Disadvantages: Still generates some harmonics and noise.
-
Applications: Household electronics, power tools, and small appliances.
3. Pure Sine Wave Inverter
-
Output: Produces a smooth sine wave identical to utility power.
-
Advantages: High quality, compatible with all AC devices, efficient and less noise.
-
Disadvantages: More complex and expensive.
-
Applications: Medical equipment, sensitive electronics, home appliances, audio/video systems.
Working Principle of Inverters
Inverters typically use power semiconductor switches like transistors or IGBTs to rapidly switch the DC input on and off, creating pulses of current. These pulses are shaped and filtered to form the desired AC waveform.
Inverter Technologies
-
Square and Modified Sine Wave Inverters: Use simpler switching methods and are easier to design.
-
Pure Sine Wave Inverters: Use advanced techniques like Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and filters to create smooth AC waveforms.
Applications of Inverters
1. Renewable Energy Systems
-
Convert DC power from solar panels or wind turbines to AC power for home use or grid feeding.
-
Key for integrating renewable energy with existing AC infrastructure.
2. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
-
Provide AC power from DC batteries during outages.
-
Protect sensitive devices like computers and medical instruments.
3. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
-
Convert battery DC to AC for driving electric motors.
-
Support regenerative braking and efficient motor control.
4. Portable Power
-
Power tools, camping equipment, and emergency power sources.
-
Allow AC devices to run from DC batteries.
5. Industrial Applications
-
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) use inverters to control AC motor speed and torque.
-
Increase efficiency and precision in manufacturing.
Summary
| Inverter Type | Output Waveform | Cost | Efficiency | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square Wave | Square wave | Low | Low | Simple tools, basic lighting |
| Modified Sine Wave | Stepped wave | Medium | Medium | Household electronics, power tools |
| Pure Sine Wave | Smooth sine wave | High | High | Sensitive electronics, medical, audio/video |
Conclusion
Inverters are essential devices that make it possible to use DC power sources in an AC-powered world. Whether powering your home with solar energy, running backup systems, or driving electric vehicles, inverters convert and control electrical energy efficiently and safely.
Choosing the right inverter type depends on the application, cost, and quality of output required. As technology advances, inverters continue to become more efficient, reliable, and widely used in modern power electronics.