What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy is the process by which a country’s central bank controls the supply of money in the economy to achieve specific economic goals. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is responsible for formulating and implementing monetary policy.The RBI’s primary goal is to keep inflation under control while supporting economic growth and ensuring financial stability. Inflation is when the prices of goods and services increase over time, making money less valuable.
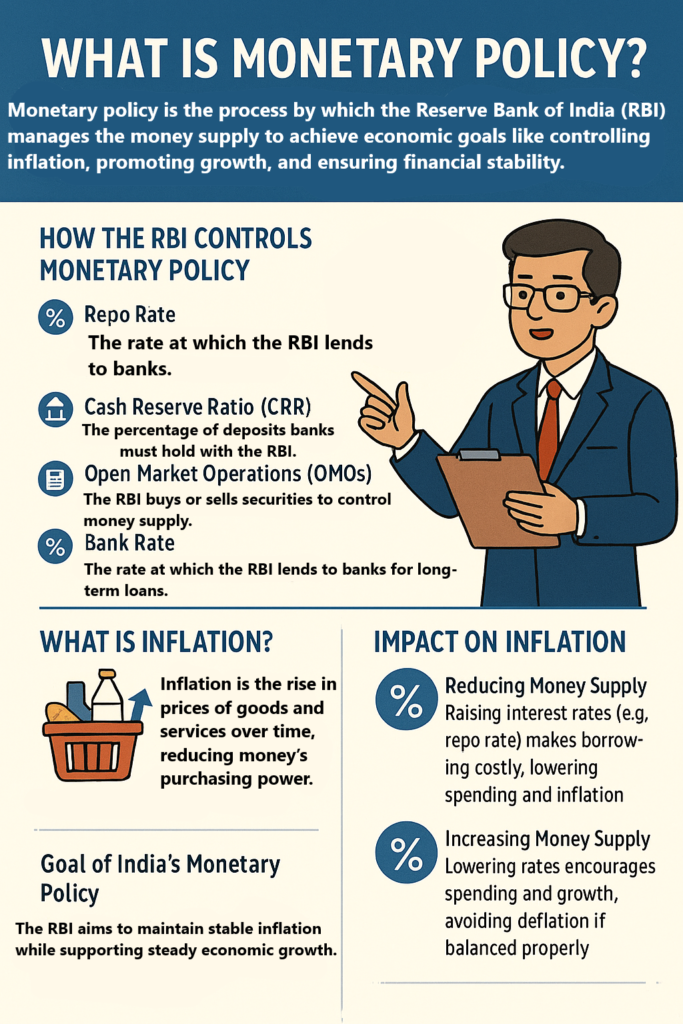
How Does the RBI Control Monetary Policy?
The RBI uses various tools to manage the supply of money and control inflation. These tools include:
- Repo Rate:
- The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks. When the RBI increases the repo rate, borrowing becomes more expensive for banks, which in turn raises interest rates for consumers and businesses.
- Effect on Inflation: By increasing the repo rate, the RBI can reduce the amount of money circulating in the economy, which helps control inflation.
- Reverse Repo Rate:
- The reverse repo rate is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from commercial banks. When the RBI raises the reverse repo rate, banks tend to park more money with the RBI, reducing the amount of money circulating in the economy.
- Effect on Inflation: By increasing this rate, the RBI can reduce money supply and help control inflation.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- This is the percentage of a bank’s total deposits that it must keep with the RBI. If the RBI increases the CRR, banks have less money to lend to customers, which can slow down economic activity and control inflation.
- Effect on Inflation: A higher CRR means less money in circulation, reducing inflationary pressures.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs):
- The RBI buys or sells government securities in the open market. When the RBI sells securities, it pulls money out of the economy, and when it buys securities, it adds money to the economy.
- Effect on Inflation: Selling securities can reduce inflation by taking money out of circulation.
- Bank Rate:
- This is the interest rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks for long-term loans. Changes in the bank rate also affect the overall interest rate in the economy.
- Effect on Inflation: An increase in the bank rate discourages borrowing and spending, which helps in controlling inflation.
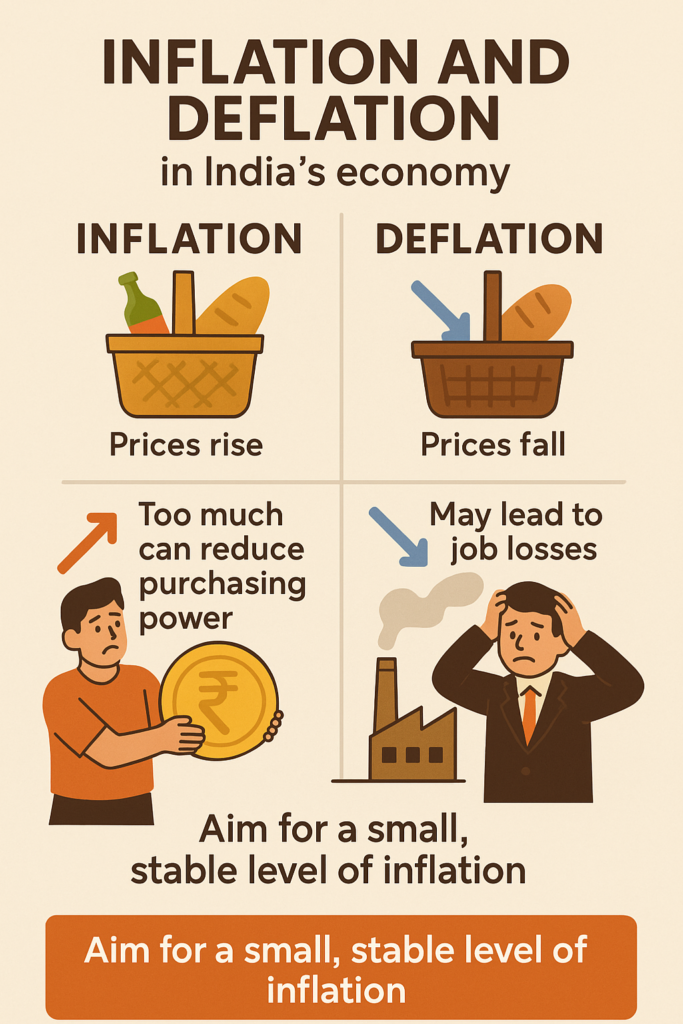
What is Inflation?
Inflation is the rate at which prices of goods and services rise over time. When inflation is high, the purchasing power of money decreases, meaning that you need more money to buy the same things.
How Does Monetary Policy Affect Inflation?
Monetary policy has a significant impact on inflation. Let’s see how it works:
- Controlling Inflation by Reducing Money Supply:
- If inflation is rising too quickly (prices are going up fast), the RBI might decide to reduce the money supply in the economy. To do this, it might increase interest rates (like the repo rate), making borrowing more expensive. When borrowing is expensive, people and businesses tend to spend less.
- Result: Less spending and borrowing means there is less demand for goods and services, which can help lower the pressure on prices and control inflation.
- Boosting the Economy by Increasing Money Supply:
- If the economy is slowing down and inflation is under control, the RBI might decide to increase the money supply. It can do this by lowering interest rates, which makes borrowing cheaper and encourages people and businesses to spend more.
- Result: More spending increases demand for goods and services, which can lead to more production and potentially higher prices (but not necessarily high inflation if the economy grows at a healthy pace).
Example: How Monetary Policy Works in Action
Let’s say inflation in India is rising too quickly, meaning that the prices of food, fuel, and other essential items are going up. This is causing people to struggle with higher costs of living.
To control inflation, the RBI may:
- Increase the Repo Rate: This will make borrowing money more expensive for banks, which will raise interest rates for loans and credit. People and businesses will borrow and spend less.
- Increase the CRR: This will require banks to keep more money with the RBI and lend out less. This reduces the amount of money circulating in the economy.
- Sell Government Securities: The RBI may sell government bonds, which will pull money out of the economy and reduce inflationary pressure.
By taking these steps, the RBI can reduce the amount of money in the economy, slow down spending, and help bring inflation down.
The Goal of India’s Monetary Policy
The main goal of India’s monetary policy is to keep inflation under control while also ensuring that the economy grows at a stable rate. The RBI tries to avoid both high inflation (which makes things expensive) and deflation (which can cause economic slowdowns).
Conclusion
- Monetary policy in India is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and is aimed at controlling inflation, promoting economic growth, and ensuring financial stability.
- The RBI uses tools like the repo rate, reverse repo rate, CRR, and open market operations to control the money supply and manage inflation.
- When inflation is too high, the RBI can take steps to reduce the money supply, making borrowing more expensive and reducing spending. When inflation is low, it can boost the economy by increasing money supply.
So, India’s monetary policy directly impacts inflation by controlling how much money is circulating in the economy and influencing spending and investment behaviors. Let me know if you need further details.