What is Government?
A government is an organization or group of people that make decisions and create laws to run a country, state, or community. The way a government operates is known as its form of government.
Three Common Forms of Government:
- Democracy
- Monarchy
- Dictatorship

1. Democracy
What is it?
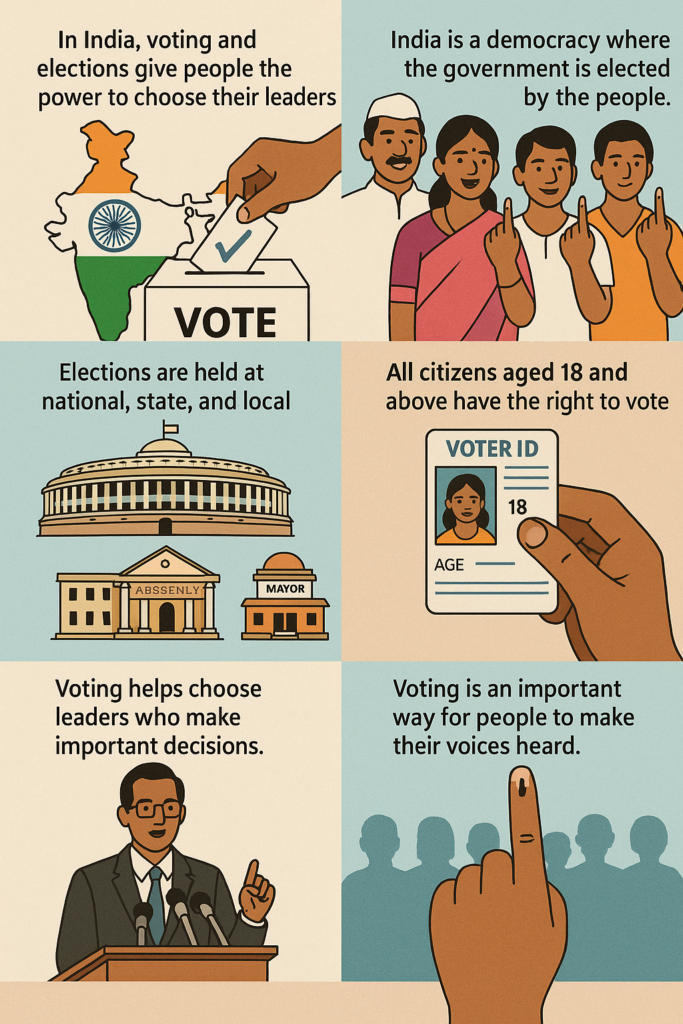
- Democracy means “rule by the people.” In a democracy, the power to make decisions is in the hands of the people.
- People in a democracy vote to choose their leaders and have a say in making laws.
Key Features of Democracy:
- Free Elections: People vote for their leaders (e.g., president, lawmakers).
- Rights and Freedoms: Citizens have basic rights like freedom of speech, freedom of the press, and the right to protest.
- Majority Rule: The majority of people’s choices or votes decide what happens, but everyone’s opinion is respected.
- Example: The United States, India, and Germany are examples of democracies.
How It Works:
- In a democracy, people can vote on laws, policies, and leaders in elections. They also have the right to participate in debates and protest peacefully.
- There are often checks and balances in a democracy, meaning no one branch of government (e.g., the president or lawmakers) can have too much power.
2. Monarchy
What is it?
- A monarchy is a form of government where a king, queen, or emperor has the most power.
- Monarchies can be absolute (where the king/queen has total power) or constitutional (where the king/queen’s power is limited by laws or a constitution).
Key Features of Monarchy:
- Inherited Power: In most monarchies, the position of king or queen is passed down from parent to child, usually within a royal family.
- Symbol of Unity: In some countries, monarchs are symbolic leaders (in constitutional monarchies), representing the unity of the people.
Types of Monarchy:
- Absolute Monarchy: The monarch has unlimited power and can make decisions without asking anyone else. Example: Saudi Arabia.
- Constitutional Monarchy: The monarch’s powers are limited by a constitution, and real political power is often with elected officials. Example: The United Kingdom, Japan.
How It Works:
- In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen makes all the important decisions, like creating laws or leading the military.
- In a constitutional monarchy, the monarch may perform ceremonial duties (e.g., attending public events), while parliaments or prime ministers handle most decisions.
3. Dictatorship
What is it?
- A dictatorship is a form of government where one person or a small group has total control over the country.
- Dictators rule with absolute power, often without the consent of the people.
Key Features of Dictatorship:
- One Leader: In a dictatorship, power is concentrated in the hands of one leader (the dictator) or a small group.
- Limited Freedom: People in a dictatorship do not have the same rights or freedoms as in a democracy. The dictator controls most aspects of life.
- No Elections: There are often no free elections, or elections are rigged to keep the dictator in power.
How It Works:
- The dictator may use force, fear, and control of the military to stay in power.
- Media and speech are censored, and the dictator might limit people’s rights to protest or disagree with the government.
- Example: North Korea is an example of a dictatorship, where one leader (Kim Jong-un) has almost all the power.
Comparing the Three Forms of Government
| Feature | Democracy | Monarchy | Dictatorship |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power | People have the power (voting). | Monarch (king/queen) holds power, but may be limited by laws. | One person or a small group has absolute power. |
| Leadership | Elected by the people (president, representatives). | King/Queen (passed down through family). | Dictator (often takes power by force). |
| Citizens’ Rights | Free speech, elections, and protests. | Limited rights in absolute monarchy, but more rights in constitutional monarchy. | Very limited rights. Freedom of speech, press, and assembly is restricted. |
| Example Countries | USA, India, France. | UK (Constitutional), Saudi Arabia (Absolute). | North Korea, Cuba, and Belarus. |
In Summary:
- Democracy: People vote and have a say in decisions, with many freedoms and rights.
- Monarchy: A king or queen rules, either with absolute power or limited by a constitution.
- Dictatorship: One leader controls everything, often with no freedoms for the people.
These are the basic forms of government that shape how countries operate and affect the lives of people in those countries. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, and the way they affect citizens can vary greatly depending on how power is used.