What is Heat in Electronics?
In any electronic device, such as your laptop, smartphone, or gaming console, electricity flows through components like processors (CPUs, GPUs) and transistors. As this electricity flows, it creates heat. If too much heat builds up inside the device, it can damage the components or cause them to work inefficiently. That’s where heat sinks and cooling systems come in—they help keep the components cool and prevent overheating.
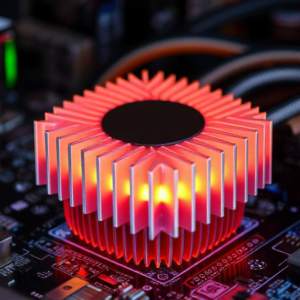
What is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink is a device that helps dissipate heat away from an electronic component. It’s like a mini radiator for your computer or phone. The goal of a heat sink is to spread out the heat generated by the component over a larger area, allowing the heat to be more easily transferred away from the device.
How Does a Heat Sink Work?
- Material: Heat sinks are usually made of materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum or copper, because they can easily absorb and transfer heat.
- Contact with the Component: The heat sink is placed directly on top of the heat-producing component (like a CPU or GPU). It absorbs the heat from the component.
- Heat Dissipation: The heat is transferred through the material of the heat sink, and then it is spread out across the fins (the metal extensions) on the heat sink. These fins increase the surface area, allowing heat to escape into the surrounding air more effectively.
- Airflow: The heat sink works best when there is airflow (such as from a fan) that helps carry the heat away.
Example:
- If you put a metal spoon in a hot cup of tea, the spoon gets hot because it conducts heat. Similarly, the heat sink “conducts” heat away from the electronics and into the surrounding air.
What is a Cooling System?
A cooling system is a broader solution used to manage and control the heat inside an electronic device. While a heat sink is a basic form of cooling, more complex cooling systems are often required in devices like high-performance computers, servers, and gaming consoles.
Cooling systems use different methods to keep components cool, including fans, liquid cooling, and thermal management technologies.
Types of Cooling Systems
- Active Cooling Systems:
- These systems use fans or pumps to actively move air or liquid to help cool the components. Active cooling is common in computers and gaming systems.
- Fans:
- Small fans are used to blow air over heat sinks and other components, helping them cool down. Fans are found in most laptops and desktops.
- Liquid Cooling:
- In more high-performance systems (like gaming PCs), liquid cooling is used. This involves a system of tubes and a liquid coolant that absorbs heat from the components and then moves it to a radiator, where the heat is released into the air.
- Liquid cooling is more efficient than air cooling and is often used in systems that generate a lot of heat, like gaming PCs or servers.
- Passive Cooling Systems:
- Passive cooling doesn’t use fans or pumps to move air or liquid. Instead, it relies on natural airflow and heat sinks to manage the heat.
- This method is quieter and simpler, but it’s usually only effective for lower-power devices like smartphones, small laptops, and other compact electronics.
- Heat Sinks: As discussed, heat sinks are part of passive cooling systems. They rely on convection (the movement of air) to transfer the heat away from the component and into the surrounding environment.
- Thermoelectric Cooling:
- This is a more advanced type of cooling, where electrical currents are used to create temperature differences. One side of the device gets cold, and the other side gets hot, allowing heat to be transferred away from sensitive components.
- This kind of system is used in high-tech applications but isn’t as common in everyday electronics.
Why Are Heat Sinks and Cooling Systems Needed?
Electronics, like computers or phones, need to operate within a certain temperature range to function properly. Too much heat can:
- Damage components: Overheating can cause parts of the device (like the CPU or GPU) to break down or wear out faster.
- Reduce performance: If the system gets too hot, it may slow down the performance of the components to avoid damage (this is called thermal throttling).
- Cause system failure: Excessive heat can cause the system to shut down or malfunction entirely.
By using heat sinks and cooling systems, we help:
- Maintain optimal performance
- Prolong the life of the device
- Prevent overheating from occurring
Examples of Heat Sinks and Cooling Systems in Devices
- Computers:
- Desktops and laptops use heat sinks and fans to cool their processors (CPUs) and graphics cards (GPUs). High-performance gaming PCs might also use liquid cooling systems to keep temperatures low during intense gaming sessions.
- Smartphones:
- Most smartphones use passive cooling (like heat sinks) to manage heat. The metal body of the phone can help dissipate heat, and some phones may use small cooling systems in their more powerful models.
- Servers and Data Centers:
- Servers that process a lot of data generate a lot of heat. They use active cooling systems, including liquid cooling and advanced fans, to keep everything from overheating.
- Gaming Consoles:
- Modern gaming consoles, like the PlayStation or Xbox, use fans and heat sinks to prevent overheating during long gaming sessions. Some high-end consoles or gaming PCs also use liquid cooling.
Challenges with Cooling Systems
- Space:
- Cooling systems, especially active ones, require space inside the device. In small devices (like smartphones), this can be a challenge.
- Noise:
- Fans, especially in high-performance systems, can be noisy. Liquid cooling systems are generally quieter but can be more expensive.
- Power Consumption:
- Active cooling systems (like fans or liquid pumps) require power to operate, which can add to the overall energy consumption of the device.
- Cost:
- Advanced cooling systems, like liquid cooling or thermoelectric cooling, are more expensive to design and implement.
Summary
- Heat sinks are passive cooling devices that help dissipate heat from electronic components by using materials that conduct heat and spread it out over a larger surface area.
- Cooling systems help manage heat in devices and come in various forms, from simple fans to more advanced liquid cooling systems.
- These systems are essential in keeping electronics cool, preventing overheating, and maintaining optimal performance.
- Active cooling uses fans and pumps, while passive cooling relies on natural airflow and heat sinks.
In short, without heat sinks and cooling systems, your electronics would overheat and fail to work properly. They are crucial for keeping devices safe, efficient, and running smoothly.