What is Fiscal Deficit?
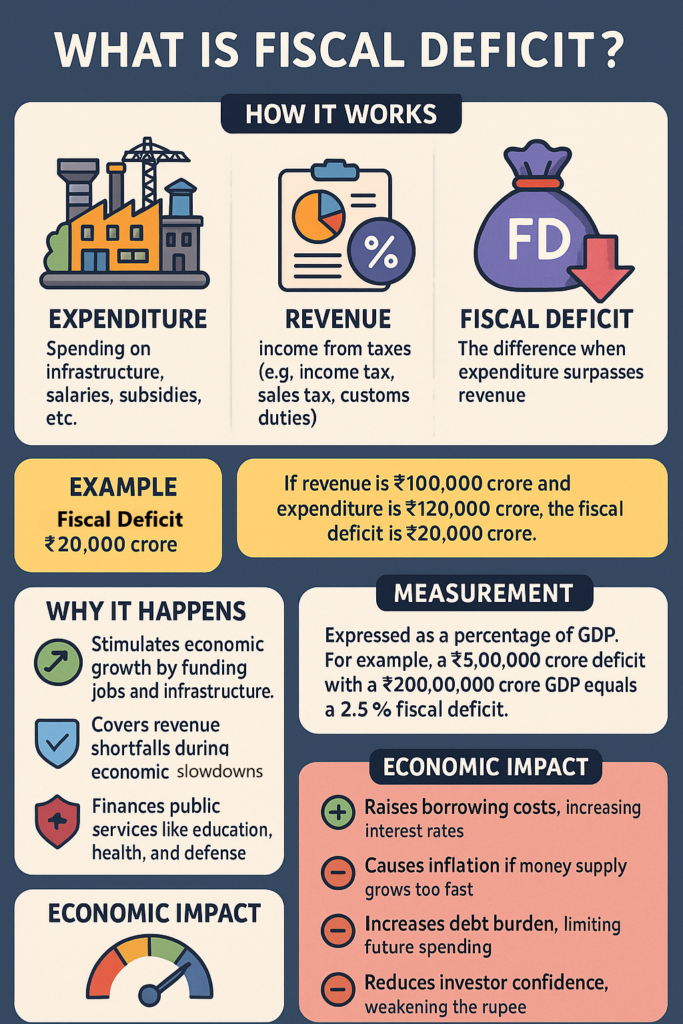
In simple terms, a fiscal deficit is the gap between the government’s total expenditure and its total revenue (excluding borrowing).
Here’s how it works:
- Expenditure: This is the money the government spends on various things, like building infrastructure, paying salaries, providing subsidies, etc.
- Revenue: This is the money the government earns, mainly through taxes like income tax, sales tax, customs duties, etc.
So, the fiscal deficit is the difference when the government spends more than it earns.
Example:
- Let’s say the government earns ₹100,000 crore in taxes and other revenues.
- But the government needs to spend ₹120,000 crore on building roads, paying salaries, healthcare, and other services.
Here, the fiscal deficit will be ₹20,000 crore (₹120,000 crore – ₹100,000 crore).
Why Does the Government Run a Fiscal Deficit?
Governments often spend more than they earn because they need to:
- Stimulate economic growth: Sometimes, the government spends more to create jobs, build infrastructure, and encourage business activity.
- Cover shortfalls in revenue: In times of economic slowdown, revenues (taxes) might be lower, so the government needs to borrow to meet its needs.
- Finance public services: India needs to spend money on various public services like education, health, defense, and social welfare, which might require borrowing.
How is Fiscal Deficit Measured?
The fiscal deficit is usually shown as a percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This is done to see how big the deficit is in relation to the entire economy.
For example:
- If the fiscal deficit is ₹5,00,000 crore and the GDP of India is ₹200,00,000 crore, the fiscal deficit is 2.5% of GDP.
Impact of Fiscal Deficit on the Economy
Running a fiscal deficit has both positive and negative impacts. Let’s look at both sides:
Positive Impacts (Why It Might Be Okay to Have a Deficit):
- Economic Growth:
- When the government borrows money (due to a fiscal deficit) and spends it, it can boost the economy. For example, spending on infrastructure (roads, bridges, etc.) creates jobs and helps businesses grow, leading to overall economic growth.
- Boosts Public Services:
- A fiscal deficit allows the government to spend on essential public services like health, education, and defense. This can improve the quality of life for citizens and promote long-term growth.
- Stimulates Demand:
- Government spending can stimulate demand in the economy, especially during slow periods. This is particularly useful in times of economic recession, where private businesses may not be investing enough.
Negative Impacts (Why a Large Deficit Can Be Harmful):
- Higher Borrowing Costs:
- If the government borrows a lot of money to cover the deficit, it could increase the demand for loans in the economy. As a result, the interest rates might go up, making it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money.
- Inflation:
- When the government borrows too much, it could lead to more money being pumped into the economy. If the supply of goods and services doesn’t increase at the same rate, this can lead to inflation, which means prices for goods and services rise, making life more expensive.
- Debt Burden:
- If the government borrows too much, it accumulates public debt. Over time, paying the interest on this debt becomes a huge burden, and the government might have less money to spend on important things like healthcare and education.
- Reduced Confidence:
- If the fiscal deficit gets too large, investors might start worrying about the government’s ability to repay its debt. This can reduce foreign investments and lead to a fall in the value of the currency (rupee). A weaker rupee can make imports more expensive.
Impact on Economic Policies:
The government uses fiscal policy (the way it collects and spends money) to manage the economy. The fiscal deficit plays a big role in shaping these policies. Here’s how:
- Budget Planning:
- The government has to plan how much it can spend and how much it needs to borrow. If the fiscal deficit is high, the government might try to reduce spending or increase taxes to bring the deficit down.
- Monetary Policy (by the Reserve Bank of India or RBI):
- The RBI might raise interest rates if the fiscal deficit is very high, to control inflation and stabilize the economy. On the other hand, if the government needs to stimulate growth, it might encourage the RBI to lower interest rates to make borrowing cheaper.
- Long-term Growth Plans:
- A country’s government might run a higher fiscal deficit in the short term to finance long-term growth plans (like building infrastructure or improving education). However, it has to ensure that this deficit is sustainable and won’t cause long-term harm to the economy.
Conclusion:
- A fiscal deficit is when the government spends more than it earns and needs to borrow money to make up the difference.
- It can help stimulate growth and improve public services, but if it gets too large, it can lead to higher borrowing costs, inflation, and a burden of debt.
- Economic policies like taxation, government spending, and interest rates are influenced by the fiscal deficit to maintain a balance between growth and economic stability.
So, while a fiscal deficit is a common and sometimes necessary tool for the government, it needs to be carefully managed to avoid negative impacts on the economy.