Angular acceleration is the rate at which the angular velocity changes. If you speed up or slow...
Physics
Coulomb’s Law: Explains how charged objects interact (either attract or repel) based on their charge and distance....
Conservation Laws are fundamental principles in physics that tell us that certain quantities remain constant (or conserved)...
Special relativity is a theory about how things move when they’re moving really fast—close to the speed...
Electromagnetic Induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field creates an electric current. It's the...
Maxwell's Equations are a set of four fundamental laws that describe how electric and magnetic fields behave...
Momentum is how much motion an object has, depending on its mass and speed. The more mass...
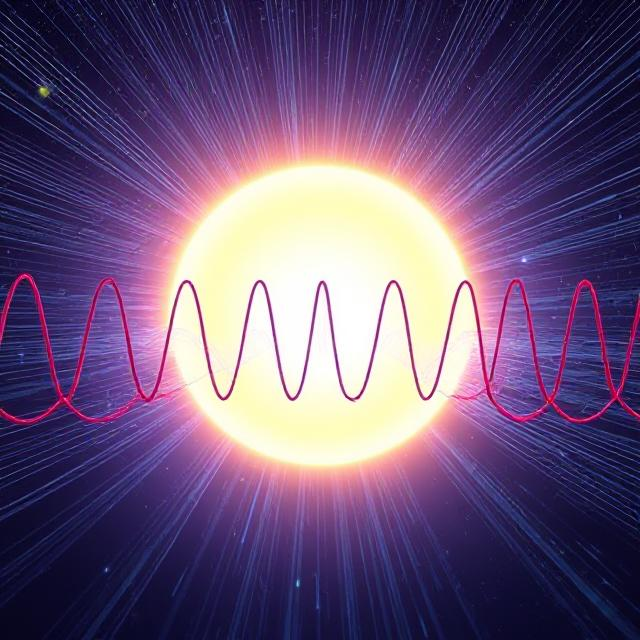
A wave is a disturbance or oscillation that travels through space and time, often transferring energy from...
Electromagnetic waves are waves that consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The wave equation tells us...
Gravitation is the force that attracts all objects to each other. Newton’s Law of Gravitation says that...
Sound is a type of vibration that travels through a medium (like air, water, or solids). When...
Projectile Motion: A type of motion where an object moves in a curved path under the influence...
Mechanics : Acceleration: Formula: a=ΔvΔta = frac{Delta v}{Delta t} Explanation: Acceleration aa is the change in velocity...
List of important physics formulas
Newton's Three Laws of Motion are fundamental principles that describe the relationship between a body and the...
Work is done when a force acts on an object and causes it to move in the...
Renewable Energy is energy that comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished by nature. These sources...
Before diving into reflection and refraction, let’s quickly understand what waves are. Waves are disturbances that carry...
Electromagnetic fields and waves are essential in our daily lives. They are a combination of electric and...
polarization refers to the direction in which waves oscillate. Most commonly, it is used to describe the...