Gravitational waves are tiny ripples in space-time, caused by some of the most powerful and energetic events...
Physics
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM): Smooth, repeating back-and-forth motion, like a swing without friction. It follows a sinusoidal...
A mechanical wave is a type of wave that needs a medium (like air, water, or a...
Optical instruments are tools that help us see things more clearly or more closely than we can...
Particle physics is the study of the most basic building blocks of matter and the forces that...
Wave-particle duality is the idea that particles, like light or electrons, can behave both like particles and...
Interference happens when two or more waves (like light or sound) meet and interact with each other....
Entropy and free energy are linked because both describe the direction in which a system moves. In...
Oscillation is simply the back-and-forth movement of an object around a central position. Oscillatory motion is periodic...
Resonance is when an object vibrates with a large amplitude because the external force matches its natural...
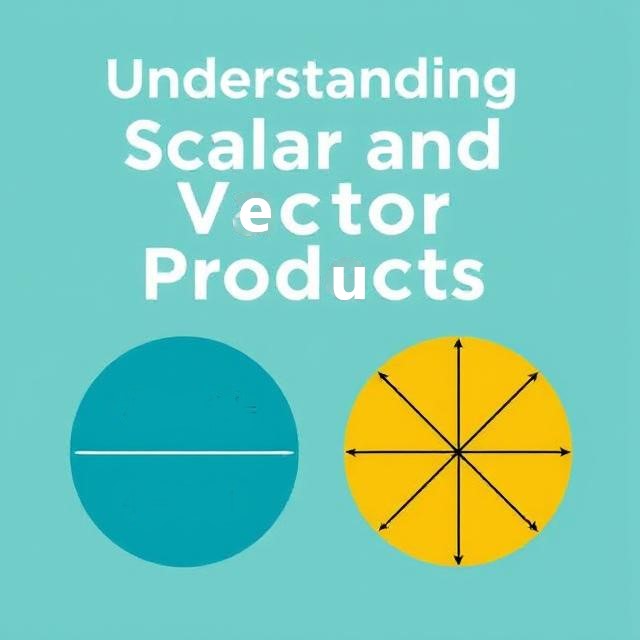
Scalar Product (Dot Product) results in a scalar number and tells you about how much two vectors...
Instantaneous speed is how fast something is moving at a specific moment in time. Instantaneous velocity is...
Phase difference refers to the difference in the phase of two waves at a specific point in...
Phase velocity is the speed at which a single wave crest (or a specific point on a...
Gauss is a unit used to measure the strength of a magnetic field. A magnetic field is...
Celsius is used globally and is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 0°C...
Planck’s constant is a fundamental number in physics that tells us how energy is related to the...
Pascal's Law explains how pressure is distributed in fluids and how small forces can be used to...
The particle nature of light refers to the idea that light behaves not only as a wave...
The Parallel Axis Theorem is a principle in physics and engineering that helps us calculate the moment...