Basic Measuring Instruments: Multimeter, Oscilloscope, Function Generator

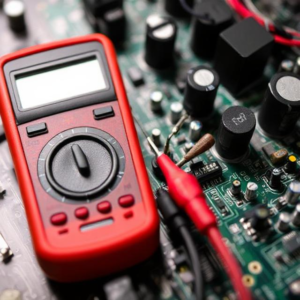
1. Multimeter
A multimeter is an essential tool used for measuring electrical values like voltage, current, and resistance. It combines multiple measurement functions into one device, making it very versatile for troubleshooting and testing electrical circuits.
-
Types of Multimeters:
-
Analog Multimeter: Uses a needle and scale to show measurements.
-
Digital Multimeter: Displays measurements on a digital screen, offering greater precision and ease of use.
-
-
Key Measurements:
-
Voltage (V): The potential difference between two points in a circuit. It can be measured in AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current).
-
Current (A): The flow of electrical charge in a circuit. It can be measured in AC or DC.
-
Resistance (Ω): The opposition to current flow in a circuit. It’s measured in ohms.
-
-
Usage:
-
To test whether a circuit is live or has power.
-
To measure the resistance of components, such as resistors.
-
To diagnose problems in electrical systems by checking continuity.
-
Multimeters are essential for both hobbyists and professionals to ensure proper functionality of electrical devices and systems.
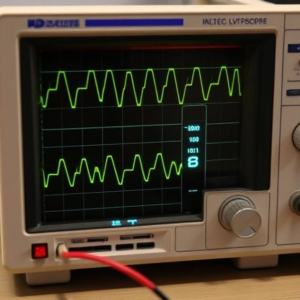
2. Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a tool used to visually display electrical signals over time. It is especially useful for analyzing complex waveforms, like those found in AC signals, communication signals, and more.
-
Key Features:
-
Waveform Display: The oscilloscope produces a visual graph of voltage over time, which helps to identify signal characteristics.
-
Time Base: Controls the horizontal axis, showing how fast the signal changes.
-
Vertical Sensitivity: Controls the vertical axis, indicating the amplitude or voltage of the signal.
-
-
Types of Oscilloscopes:
-
Analog Oscilloscope: Uses cathode-ray tubes (CRTs) to display waveforms.
-
Digital Oscilloscope: Converts the analog signal to digital data and displays it on a screen. It offers more advanced features, such as storing data and measuring frequency.
-
-
Key Uses:
-
Analyzing waveforms to identify issues like distortion, noise, or irregularities.
-
Testing and diagnosing electronic circuits, such as amplifiers or oscillators.
-
Measuring signal frequency, amplitude, and phase shifts.
-
The oscilloscope is a critical tool for engineers and technicians in fields like electronics, telecommunications, and automotive diagnostics.
3. Function Generator
A function generator is a device that generates electrical waveforms, typically sine, square, and triangular waves, at a variety of frequencies and amplitudes. It is used in laboratories, engineering, and testing environments to provide known signal sources for testing.
-
Key Features:
-
Waveform Types: Sine, square, triangle, and pulse waveforms are the most common.
-
Frequency Range: Function generators can produce signals from low frequencies (in the Hz range) up to very high frequencies (MHz or GHz).
-
Amplitude Control: Allows adjusting the height of the waveform.
-
-
Uses:
-
To simulate real-world signals for testing purposes in circuits, such as amplifiers or receivers.
-
In education, it helps students understand waveform behaviors.
-
Used in research and development to test devices like sensors, radios, and communication systems.
-
-
Applications:
-
Testing the response of circuits to specific signals.
-
Signal injection for system calibration.
-
Troubleshooting in various electronic devices.
-
Function generators are crucial in the development and testing of electronic devices, making them an essential tool for engineers.
Summary
Each of these instruments plays a crucial role in understanding, testing, and troubleshooting electrical and electronic systems:
-
Multimeter: Measures voltage, current, and resistance.
-
Oscilloscope: Visualizes the waveform of electrical signals to diagnose problems in circuits.
-
Function Generator: Produces signals for testing and development purposes.