What is Aviation and Aerospace?
Aviation
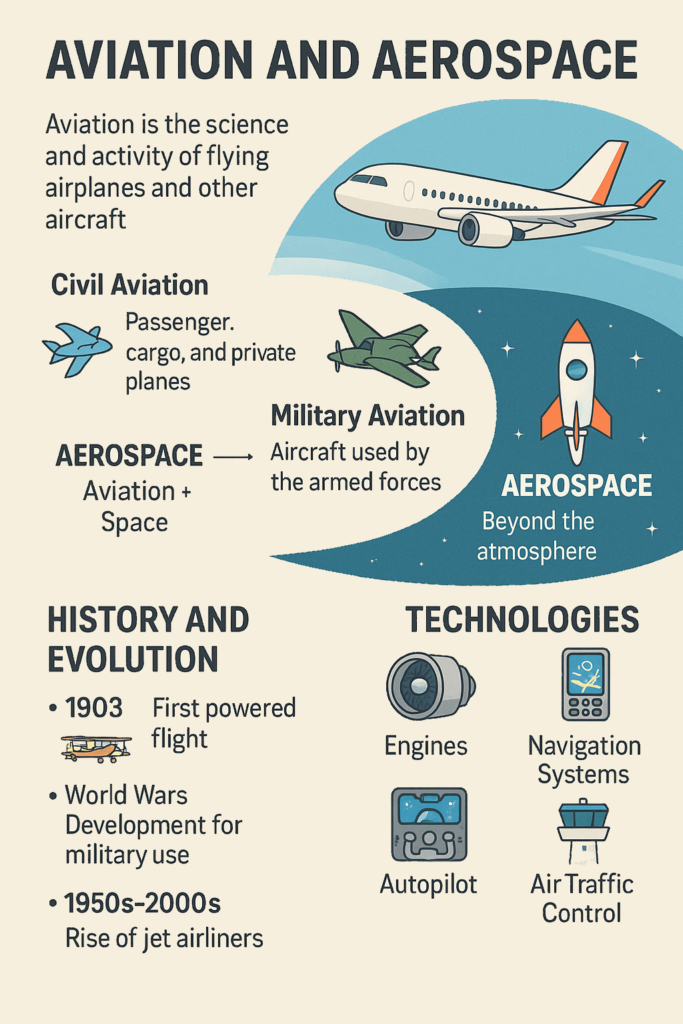
Aviation is the science and activity of flying airplanes and other aircraft within Earth’s atmosphere. It includes everything from small private planes to large commercial jets.
There are two main types of aviation:
- Civil Aviation: Includes passenger flights, cargo planes, and private planes.
- Military Aviation: Includes aircraft used by the armed forces for defense and missions.
Aerospace
Aerospace is a broader field. It includes aviation plus space travel. It covers the design, development, and use of both aircraft (planes) and spacecraft (rockets, satellites, space shuttles).
So in simple terms:
- Aviation = Flying inside the sky (in the atmosphere).
- Aerospace = Aviation + Space (beyond the atmosphere).
History and Evolution
Aviation History
- 1903 – The Wright brothers made the first powered flight in the USA.
- World War I & II – Airplanes became powerful tools for war, pushing rapid development.
- 1950s-2000s – Jet engines, passenger airliners like the Boeing 747 changed travel forever.
Aerospace History
- 1957 – The Soviet Union launched Sputnik, the first satellite.
- 1969 – NASA landed astronauts on the Moon (Apollo 11 mission).
- Today – Space travel includes satellites, Mars rovers, space tourism, and the International Space Station (ISS).
From simple gliders to space rockets, aviation and aerospace have grown quickly in just over 100 years.
Key Areas and Technologies
Aviation Technologies
- Engines: Jet engines help planes fly faster and higher.
- Navigation Systems: GPS and radar help pilots guide aircraft safely.
- Autopilot: Systems that control the aircraft automatically for smoother flights.
- Air Traffic Control: Keeps airplanes safe and organized in the sky.
Aerospace Technologies
- Rockets: Used to launch satellites and space missions.
- Satellites: Help with communication, GPS, weather forecasting, and research.
- Spacecraft: Vehicles like the SpaceX Dragon or NASA’s Orion, designed for humans or equipment.
- Rovers and Probes: Explore planets and collect data from space.
Both fields use cutting-edge science, engineering, and computers to build and control flying machines.
Careers and the Future
Careers in Aviation and Aerospace
- Pilots: Fly planes and helicopters.
- Aerospace Engineers: Design aircraft, rockets, and satellites.
- Air Traffic Controllers: Guide flights and ensure safety.
- Astronauts: Travel and work in space.
- Technicians and Mechanics: Build and maintain planes and spacecraft.
The Future
- Electric Planes: Environmentally friendly flying with electric engines.
- Space Tourism: Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are working on letting people travel to space.
- Drones: Unmanned flying vehicles for delivery, photography, and rescue missions.
- Mars Exploration: NASA and other agencies are planning human missions to Mars.
Aviation and aerospace will play a big role in how we travel, communicate, and explore in the future.
Summary:
Aviation and aerospace are exciting fields that deal with flight within Earth’s sky and beyond into space. Aviation focuses on airplanes and air travel, while aerospace includes rockets, satellites, and space exploration. These fields have developed rapidly from the first flights in the early 1900s to today’s advanced aircraft and space missions. They rely on advanced technology and offer many career opportunities, from piloting planes to engineering spacecraft. In the future, we can expect electric airplanes, space tourism, and even human missions to Mars as these industries continue to grow and shape our world.
Tags: Aerospace, Aerospace Careers, Aerospace Engineering, Air Traffic Control, Air Travel, Aircraft Technology, Astronauts, Aviation, Aviation Careers, Aviation History, Civil Aviation, Drones, Electric Planes, Engineering, Future Technology, History of Aviation, Innovation in Aviation, Mars Exploration, Military Aviation, Pilots, Satellites, Science & Technology, Science and Technology, Space exploration, space missions, Space Science, Space Technology., Space Tourism, Spacecraft, Technicians and Mechanics


